Digital concepts and online activities in blended learning
This chapter refers to blended learning as an approach that can be used for cultural peer learning activities. After a short introduction to the notions and models of blended learning, the benefits from using such an approach are presented. Moreover, useful tips of using blended learning with peer to peer activities in a digital mode are provided.
Lesson 1: What is blended learning and what are its benefits?
Blended learning is a term used to describe educational experiences that exploit both face-to-face and technology-mediated learning and interaction (Cleevelant- Innes & Wilton, 2018). Garrison & Vaughan (2008) highlight the way the two different modes are combined and describe blended learning as a “thoughtful fusion of face-to-face and online learning experiences”. With this thoughtful combination as granted, other researchers focus more on sub-aspects of the blended learning approach, stating that it can also include formal or non-formal, virtual or physical, scheduled or unscheduled activities. The key element of blended learning is the integration of the online and face-to-face components and their mutual reinforcement (Rosen & Vanek, 2020).
Noteworthy, Hannon & Macken (2014) present 3 models of blended- learning shading more light into the way physical and virtual/digital experiences can be combined.
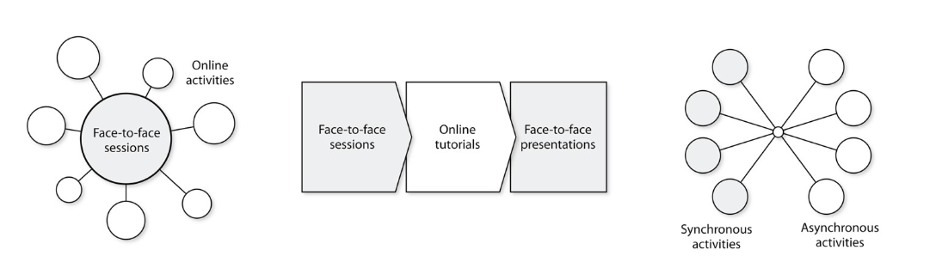
Figure x: The 3 models of blended-learning (Noteworthy, Hannon & Macken, 2014)
Model 1-Blended presentation and interaction: The first model has face-to-face interaction as its primary source of teaching. Online activities have a supplementary role, supporting face-to-face lessons. Those activities are part of trainees’ homework. Flipped classroom is the most common approach.
Model 2- Blended Block: The second model is a combination of face-to-face learning and online study divided into blocks of learning. The educator has the flexibility to design one face-to-face block which will include more intense teaching, followed by a second block with online study and so on and so forth.
Model 3- Fully online: The third model is designed only for online teaching but it consists of two parts: one with synchronous and one with asynchronous activities. In the first case there are real time online interactions between the educator and learners and in the second learners study in their own time educational material (Cleevelant- Innes & Wilton, 2018).
Various research that has been conducted highlights the benefits of blended learning approach in different contexts. In several cases it has been found:
- To be more effective than traditional face-to-face learning in terms that learners have better learning outcomes (Namyssova et al., 2019).
- It has been found to be more effective also for adult basic skills learners than only face-to-face or only online learning (Rosen & Vanek, 2020).
- Creates opportunities for learners to build digital literacy and online learning skills(Rosen & Vanek, 2020).
- Apart from that it provides flexibility and autonomy to learners, especially when they use asynchronous material and activities, it provides them the opportunity to study at their own pace (Linder, 2017).
- Blended learning promotes learners’ motivation, involving them in active learning, develops critical thinking and promotes teamwork and collaboration through peer communication (Namyssova et al., 2019). Therefore, educators are able to promote learners’ motivation provided that the course is well-designed and taught, saving time from in-person teaching at the same time.
- The designed learning material used in blended learning activities is sustainable and can be reused in the future.
Lesson 2: What online learning activities include and how to use them in peer to peer learning?
Peer-to-peer learning employs the Internet and the support that it provides to adopt its online digital form. Those forms of learning can be expanded among peers with the help of digital technology to transform the way they collaborate and exchange knowledge. Therefore, the sense of cooperation and community-orientation can be preserved in digital peer learning- if learning activities are implemented properly.
But what do those online learning activities used in blended learning include? Here are few examples:
- Synchronous and asynchronous online discussions
- Online self-assessments
- Blogs, wikis
- Virtual field trips
- Virtual labs
- Simulations
- Problem solving
- Concept mapping and interactive learning objects
- File-sharing (Google Apps such as Google docs, Spreadsheets and Slides)
- Online services for text and voice chat etc.
- Videos recorded by learners based on their expertise or experience in a field and upload those on a digital learning platform accessible to all.
- Virtual classrooms (Google classroom, Edmodo)
Last but not least, synchronous video conferencing applications- e.g. Zoom, Skype, Microsoft Teams, Webex- are very popular for the organization of peer-to-peer digital activities. They owe their popularity to their main characteristic which is interactivity. Participants are able to highly interact among each other providing to the teacher who organizes those activities the role of the facilitator. Therefore, a virtual environment is created suitable for cooperation among peers.
The use of this environment can take place when the facilitator distributes roles and tasks to learners or participants of a digital peer-to-peer activity. Initially, they should get prepared by selecting a specific topic of interest (e.g. climate action, poverty, gender equality). Then participants should employ digital tools to create appropriate content relevant to the selected topic. Cooperation may take place either in person or fully online depending on the occasion. The produced content being in a digital form it can be then uploaded to an open database allowing learners from any part of the world to have access to it. In that way cultural exchange can be promoted and the beginning of an intercultural dialogue among participants can be accomplished.
Lesson 3: Tips for a successful blended learning environment
Since the nature of blended learning allows a high degree of independence on behalf of the educator, there are several advices that could make the design of an activity easier:
- Analyze the needs of your learners. How many learners does the group have? How roles are going to be distributed to each learner especially when working with large groups?
- Consider the technological infrastructure available both for the educator and the learner. Do learners have the technological skills to perform a certain digital task?
- Consider learners’ preferences before finalizing the digital method especially when working with groups of adults.
- Do not try to fit content without adapting it for a blended learning environment first.
- Consider first the task before selecting the digital learning method that is going to be used. Planning in advance is very important to meet learners’ needs.
- Use a variety of digital tools.
- Activities in the online classroom should be interconnected with the ones of the off-line classroom.
- Promote interactivity.


